Contents
Placenta Previa: Types, Causes, Symptoms & Complications
Placenta previa is a condition that affects pregnant women. The placenta is located low in the uterus and covers the cervix. This can cause problems during labor and delivery. In some cases, the placenta may detach from the uterine wall before delivery. Placenta previa can be dangerous for both mother and baby, so it’s important to know the symptoms and treatment options.
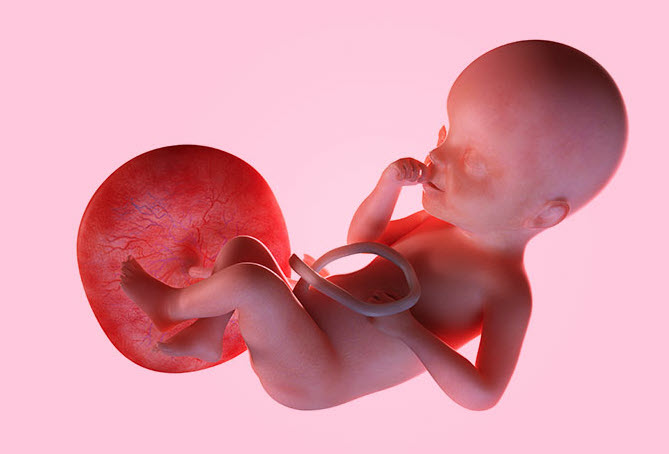
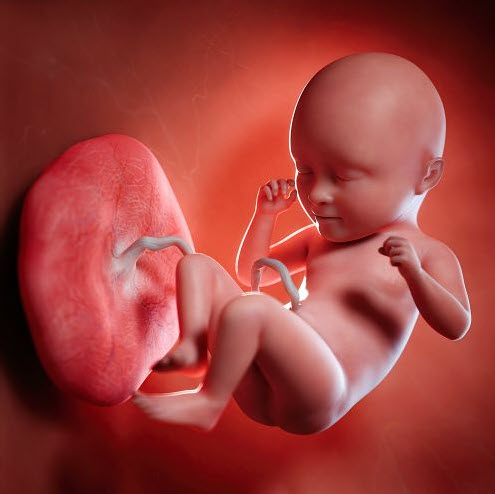
During Pregnancy baby takes its nutrients from the blood of the mother with the help of placenta. Normally this placenta is attached at the upper wall of the uterus. But when it is attached in the other part of uterus wall, it is called placenta Previa or Praevia. In the layman language, in the placenta Previa condition, placenta is in the lower segment of the uterus. Also When Placenta is attached to the front wall of the uterus, it is called anterior placenta. Similarly when Placenta is attached to the back wall of the uterus, it is called posterior placenta.
What is placenta previa?
Medically we define placenta Previa as an abnormal attachment of placenta within uterus. It is an obstetric complication where placenta attached itself on or near to cervical opening of uterus.
It is generally diagnosed in the first trimester of the pregnancy with the help of ultrasound. In most of the cases it does not create any complications and as the pregnancy progress, placenta also shifts its position in the upper wall of uterus.
Symptoms of placenta previa:
With development of diagnostic technology like ultrasound people generally knows about placenta Previa condition much before the actual symptoms and complications occur.
Spontaneous bleeding from vagina is the first symptom of placenta praevia. This bleeding is painless, and looks like fresh blood. It usually starts after 30 weeks of pregnancy, but in rare cases it can occur in first and second trimester too. About 60% of patients also complain about heavy bleeding.
Placenta previa causes:
Exact reason is still not clear that what causes placenta praevia, but there are several hypotheses which suggest that there are various conditions which increase the chances of placental attachment in cervix region.
- Scar: Scar on uterus from either previous cesarean delivery or other surgery increases the chance of placenta praevia.
- Fibroid
- Infection in lower segment of uterus
- Previous pregnancy with placenta praevia
Along with these there are other risk factors also which increases the chance of placenta previa which are as follows:
- Women with the age more than 40 years and less than 20 years are on higher risk.
- Previous Caesarean or other surgery of uterus.
- Chances of placenta praevia increases with multiple pregnancies.
- Prior miscarriage and abortion also increase risk for placenta praevia.
- Some drugs may increase risk for placenta praevia.
- Smoking and alcohol intake may increase risk for placenta praevia.
- Women pregnant with twins or triplet are great risk.
Types of placenta previa:
According to the position of placenta in the lower wall of the uterus, it has three types.
1. Complete placenta Previa:
In this type, Placenta completely covers the opening of cervix.
2. Partial placenta Previa:
Unlike the complete Previa, in this type placenta covers the some part of the opening of cervix.
3. Marginal Placenta Previa:
In this type of Previa, some placental edge ends near cervix, but not more than 2 cm of internal os.
Modern medical science divides placenta praevia into two types. This division is based upon clinical importance of placenta praevia.
- Major placenta Previa: In this type, placenta is in lower uterine segment and touches to internal os.
- Minor placenta Previa: Here placenta is in lower uterine segment but does not touched internal os.
Placenta Previa complications:
Placenta praevia is itself obstetric complication. It Increases the risk of preterm and post term haemorrhage. It also creates the risk of mortality to fetus and mother both.
1. Complications in mother:
- Bleeding in placenta praevia is maternal origin which may lead to severe hypovolemic shock or anaemia in mother. Bleeding may start on its own and may stop in sometimes also. All women with placenta praevia experience bleeding in the late second trimester or third trimester.
- Postpartum haemorrhage: placenta Previa increases the risk of high amount of bleeding after delivery which is called as post-partum haemorrhage.
- Post partum infection or puerperal sepsis: There is less amount of contraction in lower segment with placenta praevia, which increases the chance of infection in lower segment.
2. Complications in fetus:
- Intra uterine growth retardation
- Still birth (death of fetus in uterus)
- Premature delivery
Placenta Previa treatment:
Position of placenta cannot be shifted with any treatment. Aim of treatment in placenta previa is to maintain pregnancy till full term and to reduce the complications as much as possible.
Once it is diagnosed that a women has low lying placenta, then further ultrasound may be advised to track its position. It is very important to understand that as the pregnancy progresses, uterus stretches itself. Due to this stretching, position of placenta may also change to upper segment from lower segment.
If placenta previa is confirmed, then line of treatment would be:
- Reduce chances of bleeding or placental abruption: Placenta abruption is very serious condition in which placenta detaches from uterus. In placenta Previa, placenta is very prone to placenta abruption or detach from uterus. Small jerk may induce bleeding. So it is ideal to take complete bed rest. Also do not lift heavy objects as it will put pressure on the uterus.
- Delivery in placenta Previa: Mode of delivery in placenta Previa is decided by the degree of placenta, age of gestation, fetus weight and maternal condition.
If fetus and mother both are not in distress, then normal vaginal delivery may be attempted in marginal placenta previa condition. It should always be considered, even in marginal placenta previa, condition can very easily slip from hand, so senior obstetrician, anaesthetists and paediatrician should always be present nearby to manage any distress condition.
In complete placenta Previa, cesarean operation is only option for delivery as if vaginal delivery is attempted, then the delivery of placenta will happen before the baby. It will cause the life threatening situation to the baby. Hence operation should also be planned before onset of labour.
Conclusion:
If you are pregnant and experience any of the symptoms related to placenta previa, it is important to seek medical attention right away. Although most cases of placenta previa resolve on their own, there is a risk of serious complications if the condition goes untreated. Fortunately, with proper care and monitoring, most women with placenta previa can have healthy pregnancies and deliveries. We hope this article has been helpful in providing you with information about placenta previa. Thank you for reading!
Read more: Erectile Dysfunction (ED): Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
Disclaimer:
Above article is only for knowledge purpose. Please contact your healthcare provider before using any of above medicine or method. For any query or personal consultation according to your health condition please contact your doctor.