Contents
Bloody Discharge: 11 Causes
The human vagina has numerous amounts of mucus glands. Secretion from these mucus glands through the vagina is known as vaginal secretion. This vaginal discharge is made of dead vaginal and cervical cells, liquid, and some amount of bacteria. There are various types of vaginal discharge. Here we are going to explain Bloody Discharge.
1. What is bloody discharge?
Women experience typical monthly bloody discharge during their menstrual period, lasting from 1 to 7 days. Suppose you observe bloody emanating from your vaginal canal at other times, or you are bleeding during your period in a way that concerns you. In that case, you need to set up to speak with your medical professional. You, because bloody discharge in the genitals can be a sign of infection or other clinical problems.
2. When should I see a doctor regarding bloody discharge?
Periodic bleeding between periods is widespread, but you should see your doctor if it happens more than once or twice. You must see your healthcare professional right away if:
- Your bloody discharge is getting worse.
- You are over 45 years old and have bloody discharge between periods.
- You bleed after making love.
- You feel unwell, nauseous, or sick as a result of your period.
- You have abnormal vaginal discharge along with your period.
- You have a high temperature or pain during your period.
- There’s a chance you could be pregnant.
- You are menopausal.
Talking to a women’s health professional in your age group can help you feel much more comfortable if you’re worried about talking about women’s health or determining your period. Maybe you should remember that periods belong to all women, and bloody discharge from the genitals is a worry that affects most women at some point in their lives.
3. Normal vaginal secretion:
Normal discharge from the vagina is an odorless fluid that does not cause any discomfort. The amount of this can vary according to the hormonal cycle of the body, according to age, monthly menstruation cycle, and sexual arousal.
4. Abnormal vaginal secretion:
It is the most important symptom of the underlying disease. Such as milky white discharge with intense itching could be a symptom of vaginal candidiasis. Yellow discharge or green discharge with systemic symptoms like a mild fever burning micturition is a possible symptom of vaginitis or bacterial vaginosis.
Read more: Vaginal Yeast Infection: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Home Remedies
5. Bloody discharge:
Here are 11 possible causes of blood in discharge.
5.1. Bloody discharge before period:
Blood mucus discharge or spotting before actual menstruation starts is not an abnormal sign. It is due to a low level of estrogen. Normally it is just a sign of your upcoming period.
5.2. Bloody discharge after a period:
Blood coming out after cessation of menstruation is normal. It is a raiment of previous cycle blood. It usually stops within 3-4 hrs.
5.3. Menopause:
Menopause occurs between the age of 50-55. In this period, there is the fluctuation of hormones, which leads to dysfunctional uterine bleeding. Generally, it is the common phenomenon of menopause, but it is advisable to go through a clinical examination to rule out any serious medical condition.
5.4. Ovulation bleeding:
Ovulation occurs midway through your period. In this phenomenon, the ovum oozes out from the ovary, which causes minor internal bleeding. This bleeding can come out with vaginal secretion. Its color can vary from dark brown to bright red, depending upon the amount of bleeding. This bloody vaginal discharge is self-limited and does not need any treatment.
5.5. Implantation bleeding / Implantation spotting:
Fertilized ovum implants in uterus wall which causes shading of the uterine wall on implantation site. Implantation spotting is a sign of pregnancy.
5.6. Pregnancy bleeding:
Spotting bleeding within the first three months of pregnancy is the first sign of spontaneous abortion. This vaginal bleeding could be bloody discharge or bloody mucus discharge. Pregnancy bleeding is a medical emergency.
5.7. Birth control pills:
Birth control pills are a combination of female estrogen and progesterone. Accidentally missing one tablet can lead to discharge with blood. Sudden stoppage of these also interferes with the hormonal level of blood that can cause bloody discharge.
Rejection of intrauterine contraceptive device also leads vaginal discharge and bloody discharge.
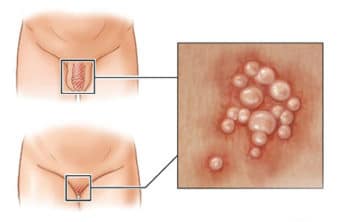
5.8. Vaginal infection and irritation:
A wide variety of microorganisms can cause vaginitis, bacterial veganism, and vaginal thrush. These infections lead to yellow vaginal discharge. Trichomoniasis and Gonorrhea are sexually transmitted diseases. Untreated cases of infection lead to vaginal ulceration and vaginal bleeding.
5.9. Rough sex or sex bleeding:
Sometimes passionate sex can lead to vaginal ulceration that causes blood in discharge. Usually, this is self-limiting and only lasts for 2-3 hours.
5.10. Cancer:
Cervical cancer has the highest mortality rate. Vaginal bleeding after sex and bloody mucus discharge from the vagina are two important signs of cervical cancer.
5.11. Ectopic pregnancy:
Implantation of fertilized ovum other than the uterine wall is known as ectopic pregnancy. This pregnancy cannot complete the full term and results in miscarriage. Profuse vaginal discharge and bloody discharge from the vagina, along with pain, are symptoms of ectopic pregnancy.
6. How is abnormal bloody discharge treated?
Your doctor will likely perform a pelvic exam and test your blood, hormone levels, and thyroid function to determine if you are pregnant or infected with a sexually transmitted disease. Likewise, imaging tests such as pelvic ultrasound, a transvaginal ultrasound, uterine ultrasound, pelvic MRI, hysteroscopy, or endometrial biopsy will help diagnose your problem. Treatment is based on the underlying cause and may include medication, fibroid softening, endometrial ablation, or medical intervention.
Treatment for abnormal bloody discharge depends on the underlying cause, as well as may include:
- Medicine.
- Birth control pills or hormone-releasing intrauterine devices.
- Uterine fibroid embolization (UFE). In this minimally invasive procedure guided by an x-ray camera called a fluoroscope, tiny particles are passed through the catheter right into the uterine arteries that are supplying blood to the fibroids, blocking blood flow and cause fibroids to shrink.
- Endometrial ablation. Guided by a narrow lighted tube with a device that when completed (called a hysteroscope), the uterine lining is destroyed using a laser or other specialized instruments that generate energy, heat, freezing, microwave energy or electrical currents.
- Muscle excision, surgical removal of fibroids.
- Expand and also cure (D&C). A treatment in which endometrial cells are delicately scraped or aspirated from the uterus.
- Removal of the uterus. A surgery in which the uterus is removed.
6. Disclaimer:
The above article is only for knowledge purposes. Please contact your healthcare provider before using any of the above medicine or method. for any query or personal consultation according to your health condition, please contact your doctor.