Contents
Jaundice (Icterus) in Babies and Adults: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
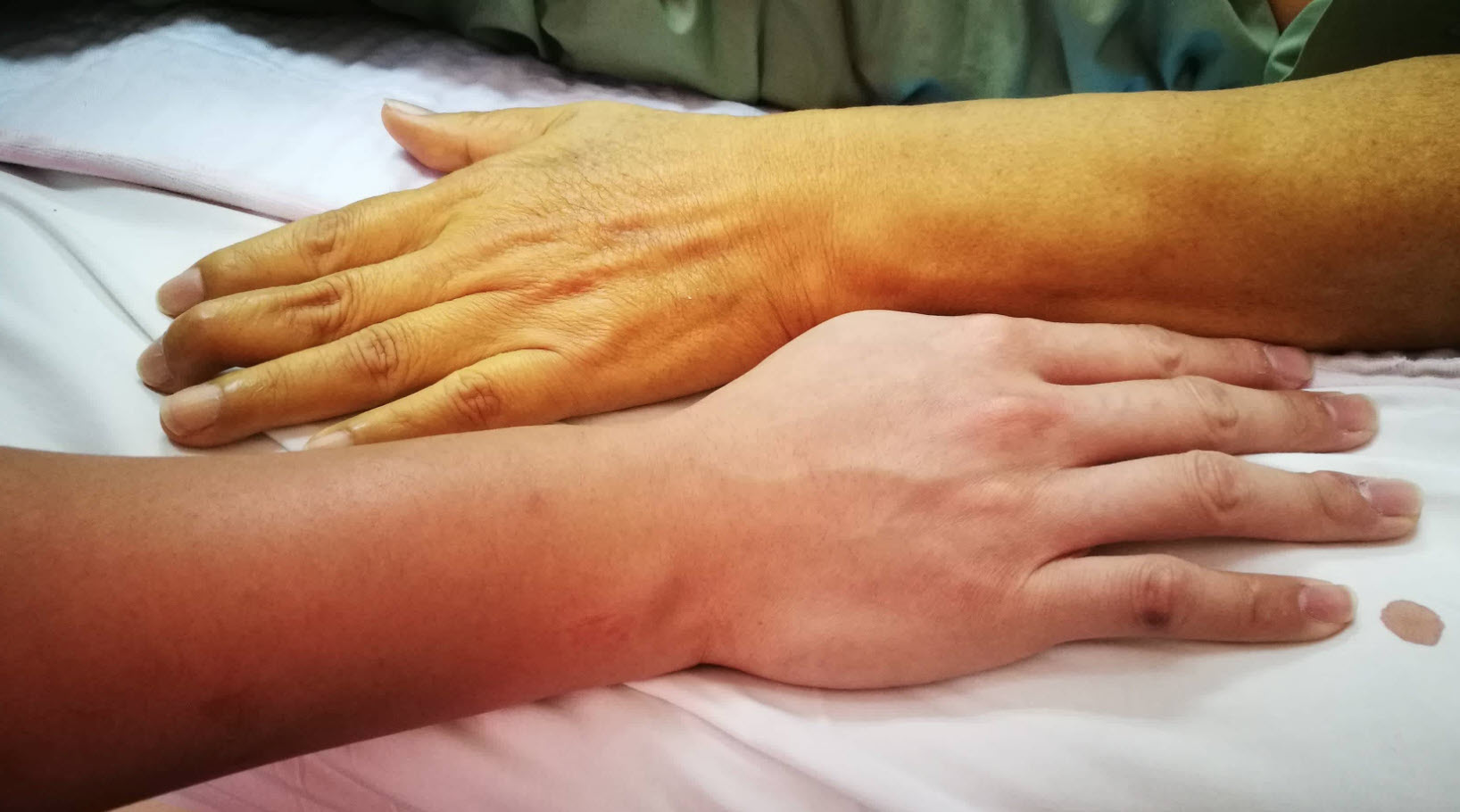
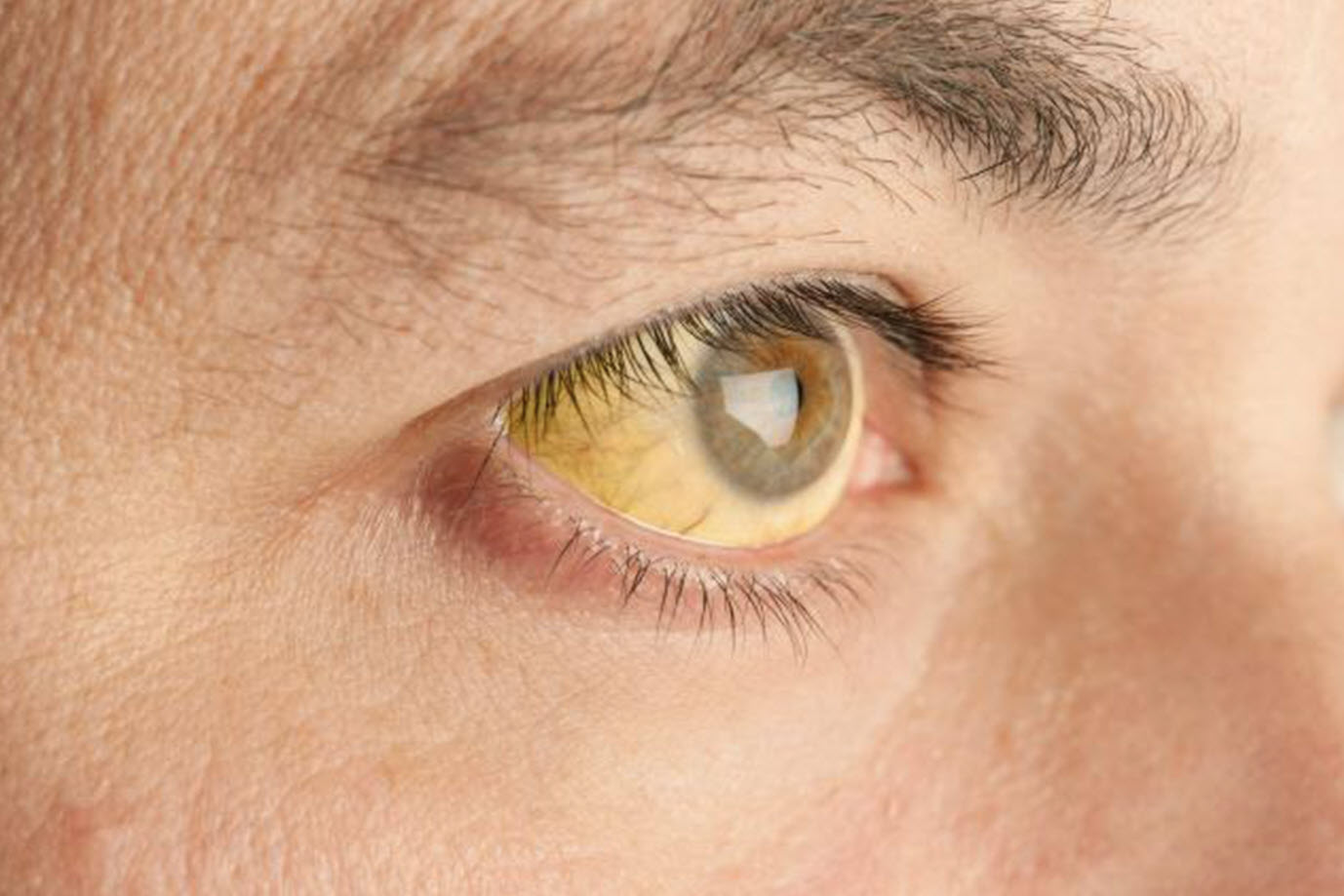
Icterus, or jaundice, is a condition that can occur in both babies and adults. It is caused by an accumulation of bilirubin in the blood, which results in a yellowing of the skin and eyes. While mild cases may not require treatment, more severe cases can be dangerous and should be treated promptly. In this post, we will look at the causes of jaundice, its symptoms and treatment options.
What is Jaundice (Icterus)?
Jaundice, also known as Icterus, is a medical condition characterized by yellowing of skin, eyes, urine and in some cases stool too. Pathophysiology of yellowing of skin is because of excessive accumulation of bilirubin in cells. When excess serum bilirubin enters in the brain and causes damage of brain cells, then this condition is termed as kernicterus.
Jaundice, also known as icterus, is a medical condition characterized by yellowing of skin, eyes, urine and in some cases stool too. Jaundice carries a characteristic odor that can be described as sweet smelling. Pathophysiology of yellowing of skin is because of excessive accumulation of bilirubin in cells. When excess serum bilirubin enters in the brain and causes damage of brain cells, then this condition is termed as kernicterus. Jaundice is a disease caused from having an excessive amount of bilirubin pigment with the blood causing it to have a yellow coloration.
This occurs due to a failure of the liver. Jaundice is not a disease on its own, but rather a symptom of an underlying condition. Jaundice occurs when there is an excessive amount of bilirubin pigment in the blood which gives it a yellow coloration. Jaundice can be diagnosed from many sources such as from the Jaundice Meter, Jaundice Gauge and Jaundice Tracker device-assisted assessment techniques.
The first sign of jaundice is seen as pale or yellowish skin tone around the belly button and eyes then it progresses upwards into the face, palms and soles until eventually fingernails and toenails will start to turn orange tinted yellow color too. In some cases stool may be yellowish in color. Jaundice can also be diagnosed from the “Jaundice Meter,” Jaundice Gauge and Jaundice Tracker device-assisted assessment techniques.
When a person suffers with hepatitis, their liver is unable to process bilirubin (a byproduct of red blood cells) into bile which then builds up inside your body causing jaundice during the hepatic failure period. Jaundice happens when there are higher than normal amounts of bilirubin in the blood. Jaundice itself is not considered a disease but rather a symptom of an underlying condition that needs to be treated, so it’s important to determine where the excess bilirubin is from in order to treat it.
Jaundice pathology:
Icterus is a medical condition of excess of bilirubin. Bilirubin is bile pigment which is formed due to catabolism of Heam (iron molecule) of RBCs in blood. This bilirubin is excreted by the liver, then concentrate by gallbladder in the form of bile juice. In the juice form, it is metabolized and excretes through stool and urine. For any reason, if this physiology is interrupted then, this excess of bilirubin in blood absorbed by cells and bilirubin gets deposited in cells and causes yellowness of cells. In starting when there is less amount of bilirubin, cells look yellow but as the disease progresses, color changes from yellow to brown and green.
Jaundice causes:
Icterus itself is not a disease, but it is a symptom of underlying disease. Underlying disease of Icterus varies from minor to fatal health disease.
1. Hemolytic Jaundice (Excess break down of red blood cells):
Due to any reason when the breakdown of RBC increases, catabolism of Heam releases bilirubin from different physiological pathways. This increases the amount of bilirubin and produces the symptoms of Jaundice. Hemolytic Icterus is generally a mild type of Icterus because the human liver is capable to excrete bilirubin load more than 6 times than normal bilirubin amount.
2. Hepto cellular jaundice (Acute inflammation of liver):
As the name suggests, It is a Icterus of hepatic origin. Liver is unable to transport bilirubin into bile. This un-transported bilirubin enters in blood and produces symptoms of Jaundice. Hepto cellular jaundice is more serious type of Icterus as in this case liver cells are being damaged.
3. Cholestatic jaundice:
Stone in bile duct obstructs the flow of bile into the intestine. There is accumulation of bile in gallbladder and liver cells. This accumulated bile gets reabsorbed in blood and causes increased bilirubin level.
4. Obstruction in bile duct:
Obstruction in bile duct due to stone, tumor, cyst, inflammation or tilt in bile duct etc. is reasons of Jaundice. This Obstruction causes stasis of bile reabsorption of bilirubin in the blood.
5. Gilbert’s syndrome:
It is a congenital disease where enzymes which are required for absorption of bilirubin are absent or deficient.
6. Crigler Najjar syndrome:
This is also a congenital condition with deficiency of the specific enzyme, related with bilirubin metabolism.
7. Dubin Johnson syndrome:
This is a serious congenital condition where liver cells are unable to excrete bilirubin.
Jaundice symptoms:
- Most common symptoms of jaundice are yellowing of the skin, conjunctiva of eyes and mucus membrane. There is also yellowish urine. In non obstructed jaundice, stool color is also yellow and in obstructed Jaundice stool color is white.
- Itchiness- bilirubin also excretes from sweat gland. This bilirubin causes itching.
Accompanying symptoms depend upon underlying disease, such as:
- Mild to moderate fever
- Abdominal pain mainly in liver side (right abdomen)
- Indigestion, especially unable to digest oil and fat
- Weight loss
- Nausea vomit
Jaundice Types:
On the basis of causative pathology, Icterus can be of three types.
- Excess of bilirubin: There is the excessive formation of bilirubin. Break down of red blood cells produces excess bilirubin. This phenomenon happens in Malaria, Spleen disease, Bone marrow disease, Thalassemia, Sickle cell crisis, etc.
- Liver cell damage: Acute or chronic inflammation of liver cells makes them unable to release bilirubin. It is a serious health condition. This phenomenon happens in hepatitis, fatty changes in liver, liver cancer and others.
- Obstruction in the flow of bile: Due to stone, tumor, tilt in the bile duct, inflammation in the bile duct and others, bile is unable to flow from the intestine. The severity of this depends upon the site of obstruction.
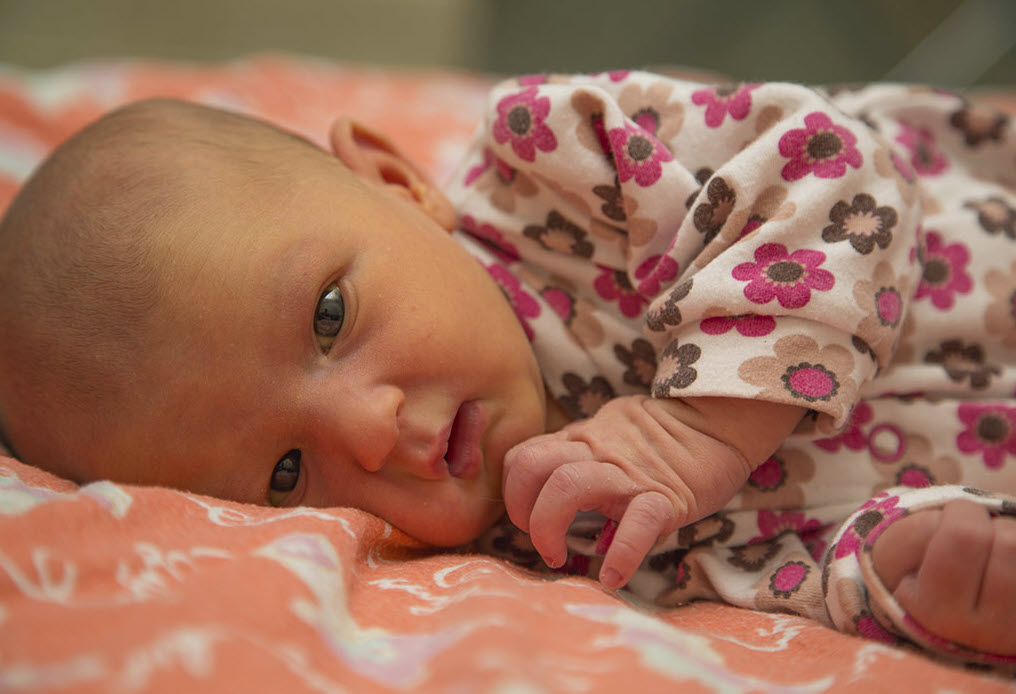
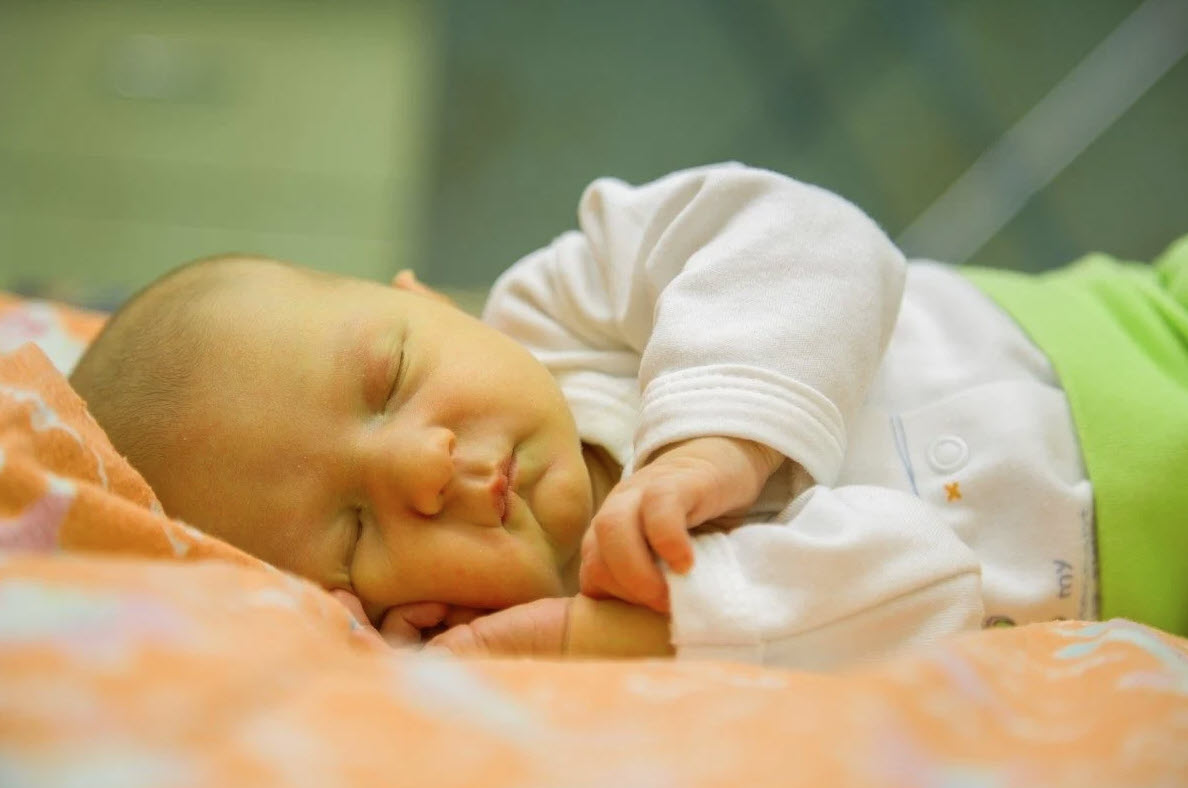
Jaundice in babies:
About 60 % of normal birth experiences Icterus in the first month of their life. Icterus in babies differs from jaundice in adult. Causes behind it, is excess of bilirubin than obstruction.
1. Neonatal jaundice:
Neonate is a medical term for babies up to the age of 1 month. Jaundice in the first month of life called neonatal jaundice. Around 60 % of birth suffers from neonatal Icterus and percentage increases up to 80 % in premature baby. Neonatal jaundice is mainly two types which are as follows:
2. Physiological jaundice in neonate:
Red blood cell of fetus is different from red blood cell of an adult. Soon after delivery, these cells break down and get replaced by adult blood cells. Moreover, hemoglobin level of fetus is 18. Soon after delivery, there is loss of hemoglobin to make a normal range of 14. These two factors cause excess of bilirubin in blood and produce symptom of jaundice. This is a physiological process and does not require any treatment. It is important to know physiological jaundice always happens from the 2-3rd day of delivery and normally resolves in 10-15 days of delivery.
a. Breast milk jaundice:
This is another type of physiological jaundice. It is not found in every child but it runs in family. Physiology behind it is unclear. Some hypotheses are there is some enzyme deficiency in milk which interferes with bilirubin metabolism. Breast milk jaundice starts on the 3-4th day and may last little longer than physiological jaundice up to 15-20 days. If baby is feeding and bilirubin level is in control limit then it does not require any treatment.
b. Breastfeeding jaundice:
Breastfeeding jaundice differs from breast milk jaundice. It is due to the insufficient feeding of baby. Due to this, there is the deficiency of calories and protein, which causes catabolism and produces Icterus like symptoms.
3. Pathological jaundice in neonate:
Pathological jaundice in neonate is a fatal condition. This is 90% due to infection or congenital obstruction in bile flow. It is serious health condition and requires urgent medical attention. Pathological Icterus occurs within the first day of baby and bilirubin level rises suddenly. It may be accompanied with other symptoms like fever, tenderness, diarrhea, breathlessness and others.
Bilirubin ranges:
Jaundice Tests:
- Serum bilirubin level: Serum bilirubin level is the first tool to diagnose Jaundice. As mentioned earlier Icterus is symptom only of the underlying disease. It requires clinical examination and lots of pathological test for confirming the diagnosis. Your doctor may advise.
- Ultrasound: To know about the size of liver, spleen, patient bile duct, stone, and others.
- Complete blood count ( CBC)
- Liver function test (LFT)
- Complete urine analysis
- Computerized tomography (CT Scan)
- Cholescintigraphy
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
- Liver biopsy
Jaundice prevention:
- Stop smoking and alcohol intake: Smoking and alcohol are related to lower immunity. Metabolism of alcohol takes place in the liver. Heavy intake of alcohol produces load on the liver.
- Prevent infection: Maintain hygiene especially with food and water. If you are on anti-biotic, please complete its course.
- Vaccination: Vaccine for hepatitis is available.
- Prevention of malaria and other hemolytic diseases.
- Avoid unprotected sex and intravenous injection.
- Most of the antibiotic and painkiller metabolism takes place in liver only. Long-term uses of these interfere with liver health.
Jaundice treatment:
Treatment of jaundice depends upon disease which is causing Icterus. After the confirmed diagnosis of the disease, health care provider will advise some treatment which can be some of these:
- Bed rest: It is watchful waiting, as the human liver has tremendous capacity to treat itself. Bed rest can ease some of the symptoms.
- IV fluid: Water consumption is necessary either by mouth or IV fluid. Fluid dilutes bilirubin and increases excretion of bilirubin through urine.
- Antibiotic: On the basis of causative factors, doctor may prescribe some antibiotics.
- Neonatal jaundice: Phototherapy is only advice.
- Surgical treatment: For removal of stone or other obstructions.
Home remedies for jaundice:
- Sugar cane juice is an appropriate diet for treating jaundice.
- Decoction of Leaves of pomegranate is beneficial.
- Amla (Gooseberry) is very good drug for treating jaundice. Consuming it in any form will help. Decoction of amala fruit, leaves, or juice of amala, etc., is a good home remedy for jaundice.
- Aloe Vera is an effective herb for treating Icterus. Consuming 15-20 ml Aloe Vera juice will remove obstruction in bile duct and maintain free flow of bile.
- Dry powder of pomegranate leaves is also capable of removing the obstruction.
- Turmeric is an excellent Ayurvedic herb for Consuming 6 gm of Turmeric with 100 ml fat-free yogurt for 15-20 days will maintain bilirubin level.
- Papaya fruit and leaves of papaya both are a good choice for Icterus treatment.
- Bitter gourd juice will ease stomach pain and obstruction of bile.
- Baking soda is an excellent choice for Icterus. It causes a chemical reaction with bilirubin (which is acidic in nature) and excretes through urine.
Conclusion:
Jaundice is a condition that can occur in both babies and adults. It is caused by an accumulation of bilirubin in the blood, which results in a yellowing of the skin and eyes. While mild cases may not require treatment, more severe cases can be dangerous and should be treated promptly. In this post, we have looked at the causes of jaundice, its symptoms and treatment options. If you think you or your child may have jaundice, please consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment.
Read more: Dysentery: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Home Remedies
Disclaimer:
Above article is only for knowledge purpose. Please contact your healthcare provider before using any of above medicine or method. For any query or personal consultation according to your health condition please contact your doctor.